This research activity endeavors the automatic detection of colon cancer in high definition colonoscopy video, by means of novel and robust computer vision-based techniques with realtime performance.
Project Goals
The aim of this approach is twofold:
- For the first time we seek to provide the experts with on-line working systems to inform them about the presence of regions of interest prone to contain colon cancer.
- In addition, we aim at making available automated analysis of the colonoscopy videos which can help to identify those traits (search patterns, reaction time, smoothness of trajectories, etc) that can be distinguishable between experts and novices in the context of colon cancer screening. This will provide the basis for the evaluation of objective and repeatable training programs for learning in the framework of skill assessment.
Our research is focused within the context of automatic quality assessment (QA) of the colonoscopy procedures by means of computer vision-based systems, in order to reduce the number of miss rates in polyp detection and, hence, to save more lives due to a pathology which is the second cause of death related to cancer in the EU.
Our aproach
In order to tackle the challenging aims proposed, and in order to overcome the still open complex technological hurdles related to these aims, our research activity goes beyond previous approaches since, for first time:
- We aim at the accomplishment of real-time colon cancer detection systems in high definition video by means of the achievement of novel and robust methods of featureextraction.
- We will apply perception studies for the characterization of saliency in colonoscopy video, in order to obtain from the experts the saliency models associated with cancer.
- We will fill the gap between the salient features in colonoscopy video (regions of interest which drive the attention of the experts) and the numerical features obtained by robust algorithms, in order to acquire a deep understanding about which are the target features to be applied to automatic colon cancer detection.
The team
Our team is in a highly privileged position to achieve the aforesaid aims through this research:
Firstly, the CVC Group bases its research activity in the two main pillars needed for the realization of the research objectives, namely:
- A long experience in diverse projects related to medical imaging, including colonoscopy video analysis
- The successful implementation of more than 49 projects for quality assessment in industrial vision, in which robustness and real time performance is mandatory. Moreover, this proposal includes the participation of researchers from the GV2 group in Trinity College Dublin, which is one of the leading groups in the area of colonoscopy video analysis, and the involvement of the Beaumont
Hospital and St. Vincent’s Hospital as EPOs.
A database for the assessment of polyp detection
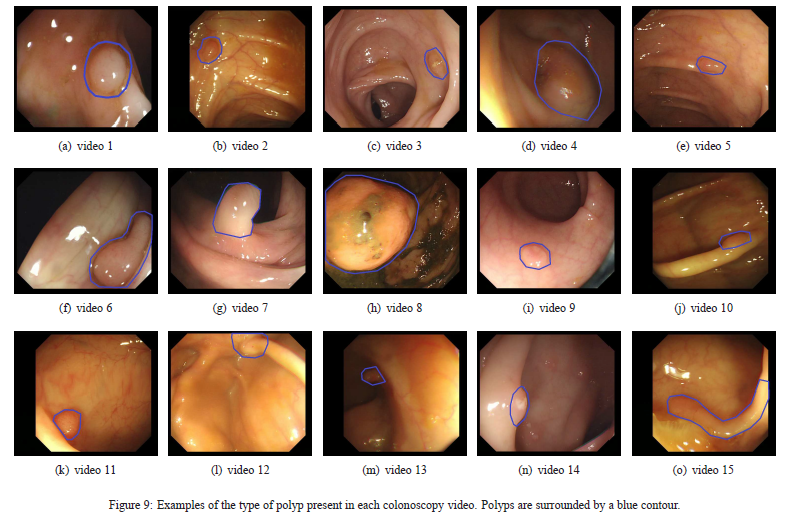
CVC-ColonDB is a database of annotated video sequences of colonoscopy video. It contains 15 short colonoscopy sequences, coming from 15 different studies. In each sequence one polyp is shown.
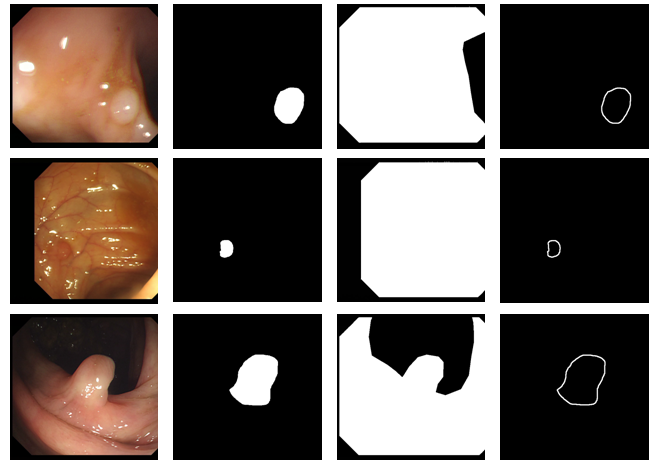
We provide an annotation of the region of interest (ROI) for 300 frames selected from all the sequences. These frames were selected in order to maximise the visual difference between them. The ROIs define the whole area covering the polyp and they are implemented as binary images, with white masks over a black background.
Database contents:
The database consists of 1200 different images, divided in four groups:
- Original .bmp files
- Polyp masks (named as p(number_of_image).bmp
- Non-informative region masks (named as s(number_of_image).bmp
- Contour of the polyp masks (named as c(number_of_image).bmp
Citation:
Jorge Bernal, F. Javier Sanchez, & Fernando Vilariño. (2012). “Towards Automatic Polyp Detection with a Polyp Appearance Model “ . Pattern Recognition, 45(9), 3166–3182.
Download:
We provide (on request) access to our colon database. For mode details, see our database description page
Project Publications and related contributions
[iframe_loader width=”100%” height=”4200px” frameborder = “0” longdesc=”” marginheight=”0″ marginwidth=”0″ name=”” click_words=”” click_url=””scrolling=”no” src=”http://refbase.cvc.uab.es/search.php?formType=refineSearch&submit=Search&originalDisplayType=Cite&sqlQuery=SELECT%2520author%252C%2520title%252C%2520type%252C%2520year%252C%2520publication%252C%2520abbrev_journal%252C%2520volume%252C%2520issue%252C%2520pages%252C%2520keywords%252C%2520abstract%252C%2520thesis%252C%2520editor%252C%2520publisher%252C%2520place%252C%2520abbrev_series_title%252C%2520series_title%252C%2520series_editor%252C%2520series_volume%252C%2520series_issue%252C%2520edition%252C%2520language%252C%2520author_count%252C%2520online_publication%252C%2520online_citation%252C%2520doi%252C%2520serial%2520FROM%2520refs%2520WHERE%2520notes%2520RLIKE%2520%2522mv%2522%2520AND%2520area%2520RLIKE%2520%2522800%2522%2520AND%2520type%2520RLIKE%2520%2522article%257Cjournal%257Cconference%257Creport%257Cmiscellaneous%257Cbook%257Cchapter%2524patent%2522%2520ORDER%2520BY%2520year%2520DESC%252C%2520first_author%252C%2520author_count%252C%2520author%252C%2520title&showQuery=0&showLinks=1&showRows=250&client=inc-refbase-1.0&citeStyle=Chicago&citeOrder=year&refineSearchSelector=notes&refineSearchName=invisible&refineSearchExclude=1&submit=Search”]